
——Guidelines for the establishment of the China Academy of Advanced Science and Technology

——Guidelines for the establishment of the China Academy of Advanced Science and Technology



Sulfur dioxide is the main component of volcanic eruption gases. In 2023, the team discovered that extreme ultraviolet photolysis can directly produce oxygen. This oxygen production pathway is believed to be an important inducing mechanism for early Earth's major oxidation events. In 2024, the team conducted in-depth experimental and theoretical research on the kinetic mechanism of sulfur dioxide extreme ultraviolet oxygen production. Yuan Kaijun and Yang Xueming's team used Dalian light source to prepare highly excited sulfur dioxide molecules, and combined with self-developed high-resolution ion imaging technology to detect excited oxygen [O2 (1)] Δ g) The quantum state distribution of the product. The experiment found that the excited state O2 product generated by the dissociation of sulfur dioxide molecules in the 133 nanometer wavelength band exhibits two types of vibrational quantum state distributions. The team led by Fu Bina and Zhang Donghui utilized a self-developed high-precision excitation state energy surface construction method and dynamic calculations of product quantum state resolution to accurately reproduce the observed phenomena in the experiment, revealing that highly excited sulfur dioxide molecules can produce O2 products with high vibrational distribution through roaming reactions, while the traditional minimum energy path only produces O2 products with low vibrational distribution. Meanwhile, experimental and theoretical evidence has shown that the roaming reaction channel contributes nearly half of the excited state O2 products.
"In the past many years, due to the lack of high brightness and tunable extreme ultraviolet light sources, it has been difficult to prepare high excited state molecules. Dalian Light Source has opened the door to studying the mechanism of molecular high excited state reactions." Yuan Kaijun said, "The dissociation of sulfur dioxide molecules by extreme ultraviolet light has produced excited state oxygen, providing a new way for the source of oxygen in the Earth's early atmosphere."
This achievement combines high-resolution experiments and high-precision theoretical research to demonstrate the first highly excited state roaming reaction channel in molecular photodissociation process, demonstrating the universality of roaming reactions in chemical reactions and providing a new perspective for exploring and predicting chemical reactions. Roaming reactions pose a challenge to traditional chemical reaction theories and will encourage scientists to develop new theoretical models and computational methods to more accurately describe and predict chemical reactions.
On February 16th, the relevant research results were published in the form of a long article titled Roaming in highly cited states: The central atom eliminations of tropical molecular composition, in Science. The research work was supported by the Science and Technology Innovation -2030 Major Project, the National Natural Science Foundation of China, and the Chinese Academy of Sciences Scientific Research Instrument and Equipment Development Project.
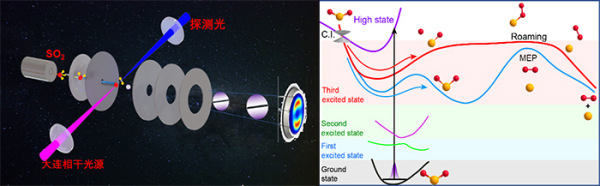
Dalian Institute of Chemical Physics discovered the first roaming reaction channel of highly excited molecular states using Dalian light source
Zhongke Frontier(Xiamen)Science and Technology Research Institute©All rights reserved
Service Customer Service:4006 285 158 Postal Code:361006
Address:Science City Zhongke Building,Huangpu District,Guangzhou City
396 Jiahe Road,Huli District,Xiamen City
Website:http://www.zk-yjy.com